搜索到 1000 条关于 m68유흥오피DB문의-~텔ErrorBased⑁II 的文章
-

-
2016.12.14 距肛缘 10~15 cm 的直肠癌应定义为结肠癌
和直肠肿瘤的生物学特性存在差异,制定划分的明确标准对于科学研究和临床治疗都是非常必要的。Breugom 等在 Lancet Oncol 发表的系统综述提示 II...可能受益(1)。Andre 等的研究显示 III 期和高风险 II 期结肠癌患者受益于辅助化疗(2),因此有争议是否将肿瘤距肛缘 10~15 cm 的直肠癌划归
-

-
2018.07.16 Seth Podolsky, M.D. 克利夫兰医学中心国际业务发展和医院运营部医疗总监、医学博士
Seth Podolsky, M.D. 克利夫兰医学中心国际业务发展和医院运营部医疗总监、医学博士Dr. Seth Podolsky 作为医疗负责人,为克利夫兰医学中心国际化业务拓展提供支持。此外,Dr. Seth Podolsky 还担任克利夫兰医学中心急诊科负责人,统筹克利夫兰医学中心在俄亥俄州东北部医院和家庭
-

-
2016.06.08 FDA 批准新的诊断造影剂 Netspot 用于罕见神经内分泌瘤检查
6 月 1 日,美国 FDA 批准 Netspot,该产品是首个用于镓 [68 Ga] 奥曲肽注射剂制备的套装,68 Ga 奥曲肽注射剂是用于正电子放射断层...抑制素受体阳性神经内分泌肿瘤有生长激素抑制素受体,它是一种调节内分泌系统的激素。68 Ga 奥曲肽是生长激素抑制素的一种正电子发射类似物,它通过与这种受体连接
-

-
2014.12.20 我们到底能不能用上新药?
时间差:晚72个月赫赛汀通用名:曲妥珠单抗药品描述:用于人类表皮生长因子受体II的单克隆抗体,是治疗HER-2阳性表达乳腺癌的主要药物。FDA批准时间:1998年9... Data 数据库 (db.dxy.cn)本文来自丁香园微信
-
-
2018.06.06 神经综述:手足口病的神经系统并发症
阴性。来自台湾的一项研究发现,EV71 中枢神经系统受累最突出的症状为肌阵挛性抽搐(68%),呕吐(53%),共济失调(35%)和震颤(21%)。EV71..., Song Y, Zhao L, Luo K, Zhang M, Feng L, Yang L, Sheng X, Fan X, Xiao
-
2012.06.14 2012年度中韩合作与交流项目获批名单公布
数理II-VI/IV 芯-SiO2 鞘纳米线可控制备和顶栅场效应晶体管
-
2012.07.24 高神经酰胺水平增加阿尔茨海默病风险
家Michelle M. Mielke博士说:“我们的研究所明确的这一生物标志物可以作为一个潜在的预防和治疗阿尔茨海默症的新靶点。”在研究的当...在“妇女健康和年龄研究II”中测定他们血液当中的血清神经酰胺含量水平,神经酰胺是一种遍布全身的脂肪化合物,与炎症和细胞死亡有关。受试者被分为三组
-

-
2018.07.16 Tomislav Mihaljevic, M.D. 克利夫兰医学中心首席执行官兼总裁、医学博士
Tomislav Mihaljevic, M.D. 克利夫兰医学中心首席执行官兼总裁、医学博士Tomislav Mihaljevic 负责领导克利夫兰医学中心主院区、11 家区域医院、18 个家庭医疗中心以及位于美国佛罗里达州与内华达州、加拿大多伦多、中东阿布扎比和英国伦敦的医疗机构。Dr. Mihaljevic
-

-
2019.12.28 避免 LC 术中胆管损伤,掌握这 6 点就够了
1985 年德国医师 Mühe 在直视镜下进行了首例腹腔镜胆囊切除术(LC)。在1992 年,美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)达成专家共识,认为除了... 2013》(TG13)中,LC 适用于 I 级(轻度)和 II 级(中度)AC,对于 III 级 AC,建议在胆囊引流后择期进行。但在《东京指南 2018
-

-
2020.12.23 发热半月余的骨髓肉芽肿,病原会是什么呢 ?
病情介绍患者,女,68 岁,江西省上饶市人,因「反复发热半月余」于 2015-11-16 入院。患者入院前半月余出现发热,最高体温 39℃,伴有畏寒寒颤,夜间...,可见类上皮样细胞增多,上皮样结节形成,网染(-),提示肉芽肿形成(图 1)。免疫组化染色结果:MPO(粒+)、CD20(个别+)、CD3(-)、CD68(部分
-
2019.11.26 国际实战专家与您探讨 ICH Q3/M7关于药物杂质的最新预期监管要求与难点解析
析出物和可提取物品:与包装有关的杂质问题基因毒性杂质,ICH M7解读案例研究:缬沙坦案例与法规回应解析课程大纲第1天课程将从ICHQ章节所涵盖的原料降解物...和可提取物它们是什么?为什么要关注它们?容器封闭系统化合物的迁移理解相关的复杂法规框架,特别是新版USP通用章节的潜在影响 第2天第二天将专注于讨论ICH M
-

-
2014.08.08 Insight 数据分析:2014 年 7 月 CDE 药品审评报告
INSIGHT-China Pharma Data 数据库统计,7月份CDE 共承办化药进口新申请以受理号计有 68个,涉及46个品种,与上个月相比略有增加。其中...:INSIGHT-China Pharma Data 数据库(http://db.dxy.cn)是由丁香园专业团队打造的医药行业综合数据库平台,为药品研发机构、市场销售
-

-
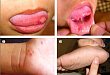
2013.07.22 原发性干燥综合征患者的眼睑肿胀一例
-

-
2013.05.20 AR:晚期莱姆病的趾炎
mily: 'Helvetica Neue', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; font-size: 14.399999618530273px; line-height: 20px;">患者女,77岁, 一年前开始出现右足第三趾肿大伴蓝色斑点,症状逐渐加重。之前的两项风湿病学评估和足部磁共振成像提示第一、第三及第五足趾腱鞘炎,但不足以明确诊断。临床检查发现右足比左足大。除第三趾的蓝色趾炎外,患者的足内外边界也有红色/蓝色斑点。
-

-
2015.08.27 老年 2 型糖尿病患者首选二甲双胍治疗获益更佳
ccvideo患者信息:患者,女,68 岁,糖尿病病程 9 年。主诉:多饮、多尿、消瘦 9 年,视物模糊 1 月。现病史:1 月前空腹血糖 9.2 mmol/L,餐后 2 h 血糖 18.5 mmol/L,服用「亚莫利」「拜糖平」治疗 1 个月,空腹血糖 9.5 mmol/L,餐后 2 h 血糖 17.82
-

-
2016.05.05 2016AAN: NMDAR抗体在自身免疫性脑炎中发挥重要作用
Josep Dlmau教授在68届美国神经病学会(AAN)年会上的发言指出,自 2007 年在一组表现为记忆障碍、精神障碍和通气不足的病人中发现针对 N-甲基... E, Horvath J, Shiloh-Malawsky Y, Sangha N, Martinez-Lage M, Dalmau J. Analysis
-

-
2020.01.06 ETV 治疗出现骨损伤换用 TAF 治疗体会
:29.7kpa,CAP:213dB /m。患者入院后询问病史得知:既往史、家族史均无特殊。完善辅助检查:血常规、尿常规均正常,肾功能正常。甲丙丁戊嗜肝性病...显增加,B 超检查同前无明显变化。Fibroscan:8.9kpa,CAP:223dB /m。HBVDNA<20IU/ml(罗氏诊断)。检查骨密度、血钙、血磷

