搜索到 1000 条关于 59s문발디비업자상담)II텔contiTEAMII➡️ 的文章
-

-
2013.05.27 回复:妇产科中级考试归来!
1.TBS分类:见不典型鳞状细胞:鳞状上皮异常 2.最常见的尿瘘:膀胱阴道瘘 3.SUI:压力性尿失禁 4.18岁少女,有原发性痛经:用前列腺素合成酶抑制剂 5.不属于垂体性闭经:PCOS 6.雌激素水平低落:II度闭经 7.还考了两张B超图,根据子宫内膜情况,决定治疗用药,有点...
-

-
2012.10.01 回复:请考完副主任医师的战友来晒晒题
1.宫颈外口已脱出阴道口:子宫脱垂II轻 2.子宫脱垂鉴别诊断有:宫颈延长;阴道壁肿物;粘膜下肌瘤 3.绝经2年HRT治疗:雌孕激素序贯应用 4.外阴硬化性苔藓:外阴肛周皮肤萎缩变薄 5.外阴硬化性苔藓:治疗丙酸睾酮油膏 6.外阴鳞状细胞癌:最常见的外阴癌 7.经前期综合征治疗:...
-

-
2012.06.25 口服干扰素加注射利巴韦林治疗丙肝的2期临床试验获阳性结果
2012年6月14日,赛德医药科技和阿马里诺生物科技(OTCBB:AMAR)发表声明,其产品在台湾丙型肝炎病毒感染患者上进行的剂量范围II期临床研究得到了阳性的结果。一共169名病人(1b基因型)随机地服用500或1500国际单位(IU)天然人α干扰素(IFNa)口含片或相应的空白片24周,接下来24周不服药并进行观察。所有接受IFNa和Ribavirin注射24周的病人 ...
-

-
2018.07.06 脑深部电刺激治疗阿尔茨海默病的初步探索(上)
图 1 封面图片阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disorder, AD)是一种中枢神经系统原发性退行性疾病,全世界约有 4600 万人患有痴呆症...(NCT01608061)临床试验研究结果已在《Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease》发表。Ⅰ期临床试验已证明 DBS 能够调节功能异常的
-
2012.09.19 【免注册费】上海分子流行病学与GWAS会议国际研讨会
分子流行病学再揭示人类复杂疾病遗传因素及其与环境因素相互作用发挥重要作用,为人类疾病的风险评估、预防和个性化治疗提供依据。全基因组关联分析(GWAS)为全面系统研究复杂疾病的遗传因素掀开了新的一页,为我们了解人类复杂疾病的发病机制提供了更多的线索。科学家已经在肥胖、糖尿病、冠心病、阿尔茨海默、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、肺癌、胃癌等一系列复杂疾病中进行了全基因组关联研究并找到疾病相关的易感基因,我国科学家也在银屑病、精神病和冠心病等方面开展了GWAS研究并取得成效。国家科技部最新公布了“常见重大疾病全基因组关联分析和药物基因组学研究”的863重点项目,吹响了我国大规模开展GWAS研究的号角。为了让更多的相关研究人员,特别是广大研究生了解GWAS的研究原理和方法,学会设计GWAS的研究和分析实验结果,同时在癌症领域分享海内外研究专家们的成功经验,并期待在GWAS方面进行交流合作,复旦大学和美国Van Andel 研究所将于2009年7月12-14日在上海联合举办上海分子流行病学与GWAS国际 研讨会, 期待各位同道免费参加,请有意者及时将回执返回联系邮箱。免注册费(食宿餐饮费用自理)。名额有限,报名从速!时间: 2009年7月12-14日
报到地点: 复旦大学卿云楼宾馆 上海市邯郸路220号,200433
会议地点: 复旦大学逸夫楼报告厅
联 系 人: 赵雪莹 高歌 联系电话: 021-55664495
回执邮箱: GWAS2009@gmail.com
BackgroundRecent success of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in the U.S. and Europe has lead to the identification of a large number of genetic variants that are associated with disease risk and progression, including those for cancer and cardiovascular diseases. The discovery of these genetic markers not only improves our understanding of disease etiology, but also contributes significantly to risk prediction, early detection, and targeted treatment of diseases.Although GWAS have been used in Chinese populations to identify Chinese-specific risk-associated genetic variants for several common diseases such as breast cancer and psoriasis, many more GWAS are needed for various diseases. A better understanding of the importance of GWAS and a better knowledge of study design and data analysis of GWAS will further promote broad application of GWAS in China. This symposium which will cover genetic epidemiology and GWAS in China is organized to serve this purpose. We have invited a group of experts in this area from the U.S. and China to share their experience in GWAS, and we hope to foster an environment which will encourage an open discussion among all participants.
Objectives• To better understand the potential applications of GWAS
• To address practical issues in study design, implementation, and data analysis of GWAS
• To promote interaction and collaboration among researchers who are interested in GWAS
• To explore other important studies after GWAS: gene-environment interaction, risk prediction, and functional analyses
• To consider issues and implications related to genomic and personalize medicine
Organizing committeeThe organizing committee consists of four members:
Dr. Jianfeng Xu (Co-Chair)
Dr. Daru Lu (Co-Chair)
Dr. Li Jin (Co-Chair ,Advisor)
Dr. Qingyi Wei (Co-Chair, Advisor)
PresentationsSession I: Genetic epidemiology and GWAS of cancer
• Breast cancer in Chinese populations Xiao-ou Shu
• Genetic association studies of skin cancer Jiali Han
• Genetic variants in the MC1R gene and risk of cutaneous melanoma Qingyi Wei
• Genetic association studies of lung cancer in Chinese populations Daru Lu
• Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocarcinoma Gangqiao Zhou
• Molecular epidemiology of stomach cancer Weimin YeSession II: Genetic epidemiology and GWAS of other diseases
• Genetic association studies of hypertension in Chinese populations Jiang He
• GWAS of Autoimmune Diseases (Psoriasis, etc.) in Chinese populations Wei Huang
• Molecular epidemiology of diabetes in Chinese populations Weiping Jia
• Molecular genetics study of hypertension in Chinese populations Dingliang Zhu
• Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocarcinoma Gangqiao ZhouSession III: Post-GWAS studies
• Genetic structure of Chinese population Li Jin
• High-throughput genotyping for GWAS and fine mapping studies Siqun Lilly Zheng
• Molecular genetics study of neural tube defect Hongyan Wang
• Risk prediction using genetic variants in prostate cancer Jianfeng Xu
• Gene-environmental interaction in smoking related cancer Zuo-Feng Zhang
• Cancer Somatic Genomics Bin TehSession IV: Short presentations by participants and discussion
Registration时 间: 2009年7月12-14日
报到地点: 复旦大学卿云楼宾馆大厅 上海市邯郸路220号 (200433)
会议地点: 复旦大学逸夫楼报告厅
联 系 人: 赵雪莹,高歌 (Shanghai, China);Tamara Adams (U.S.)
联系电话: 21-55664495 (Shanghai, China);336-713-7532 (U.S.)
回执邮箱: GWAS2009@gmail.com (Shanghai, China);tsadams@wfubmc.edu (U.S.)
Invited speakers (alphabetic)• Jiali Han, Ph.D., is an Assistant Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. His major research areas are:
• Genetic epidemiology of skin cancer and breast cancer
• Genome-wide association studies
• Gene-environment interaction• Jiang He, M.D. Ph.D., is a Professor and Chair of Epidemiology, Tulane University School of Public Health., U.S.A. His major research areas are:
• Genetic epidemiology of hypertension
• Gene-nutrition interaction of cardiovascular disease• Wei Huang, Ph.D., is a Professor and Executive Deputy Director of Chinese National Human Genome Center at Shanghai, China. Her major research areas are:
• Genetic susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
• Genome-wide association studies
• Genetic variants and association study• Weiping Jia M.D., is a professor of endocrinology at Shanghai Institute of Diabetes, Shanghai No.6 People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Her major research area is:
• Molecular endocrinology and diabetes• Li Jin, Ph.D, is a Professor of Genetics and vice President of Fudan University, China. His major research areas are:
• Genetic and molecular epidemiology of lung cancer and glioma
• Genetics of metabolism diseases
• Genetic markers for population genetics• Daru Lu, Ph.D, is a Professor of Genetics and Vice Dean of School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, China. His major research areas are:
• Genetic and molecular epidemiology of lung cancer and glioma
• Genetics of metabolic disease• Xiao-ou Shu, M.D, Ph,D, is a Professor of Medicine in the Department of Medicine at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, U.S.A. Her major research areas are:
• Genetic and lifestyle predictors of cancer and other chronic diseases
• Cohort study methodology
• Incorporating biomarkers in risk prediction• Bin Teh, M.D, is a Distinguished Scientific Investigator at Van Andel Institute, U.S.A. His major research areas are:
• Translational cancer research
• Gene expression profiling
• Cancer genome high-throughput sequencing• Hongyan Wang, Ph.D, is a professor of genetics at School of Life sciences, Fudan University, China. Her major research area is:
• Molecular genetics and epidemiology of birth defects (deformity of neural tube, congenital heart disease, etc.)• Qingyi Wei, M.D, Ph.D, is a Professor of Epidemiology at The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, U.S.A. His major research areas are:
• Molecular epidemiology of DNA repair, apoptosis, and skin cancer and head and neck cancer
• Genetic susceptibility to cancer
• DNA repair and apoptosis phenotype markers• Jianfeng Xu, M.D, Dr.PH, is a Professor of Epidemiology and Cancer Biology and Director of the Center for Cancer Genomics at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, U.S.A. His major research areas are:
• Genetic epidemiology of prostate cancer
• Genome-wide association and fine mapping analysis
• Risk prediction using genetic markers and other clinicopathologic variables• Zuo-Feng Zhang, M.D., Ph.D, is a Professor of Epidemiology at UCLA School of Public Health, U.S.A. His major research areas are:
• Molecular epidemiology of smoking-related cancers
• Confirmation studies of SNPs identified in genome-wide association studies in smoking-related cancers
• Gene-environmental interaction between genetic markers and environmental factors• S. Lilly Zheng, M.D, is a Professor of Medicine and Director of the Genotyping Laboratory at Wake Forest University School of Medicine. U.S.A. Her major research areas are:
• High-throughput genotyping and sequencing
• Genetic epidemiology of prostate cancer• Gangqiao Zhou, Ph.D, is a Professor of Medical Genetics and Genomics in National Academy of Military Medical Science. His major research area is:
• molecular and genetics of complex diseases• Dingliang Zhu, M.D, is a professor of cardiology at Shanghai Institute of Hypertension, Shanghai, China. His major research area is:
• Molecular and genetics of cardiovascular diseases• Weimin Ye, Ph.D, is a Professor of Medical Epidemiology at Karolinska Institutet, Sweden. His major research areas are: Etiology of upper gastrointestinal diseases
• Topic of presentation: Molecular epidemiology of stomach cancer
-
2012.09.19 2012第二届生物能源大会
论坛5:生物质原料(II):能源作物专场500:生物能源作物的高效基因改良...507:多年生能源植物Track 5: Biomass Feedstock II: Dedicated
-
2017.10.20 2017 实用超声诊疗规范学习班
随着超声医学的普及,超声扫查的标准化、诊断的规范化对于超声医师的重要性日益凸显。临床医生对超声技术的适应症、检查诊断优势、对临床的决策影响等仍不足,为进一步普及和推广妇产儿科超声诊断技术,规范诊疗行为,促进学术经验交流,特举办「2017 实用超声诊疗规范学习班—妇产儿篇」,参会代表可获得市级继续教育 II 类学分 8
-
2009.10.16 孙燕:在既往接受治疗的晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者中,比较Vandetanib联合多西赛与多西他赛的III期研究(ZODIAC)
丁香园驻地通讯员报道:在2009CSCO年会上,中国医学科学院肿瘤医院孙燕院士回顾了Vandetanib I、II期研究成果。通过对全球>4500晚期NSCLC患者的研究数据表明,Vandetanib的剂量最多达到300ng,耐受良好,不良反应多为轻度,并可通过调整课题而减少。最常见的不良反应包括皮疹、腹泻等
-

-
2014.11.11 帕金森氏病与脂肪瘤
(II-5)为58岁印度女性;49岁时患有左侧运动不能-强直综合征和重度抑郁;52岁时接受治疗(罗匹尼罗8mg/天,左旋多巴300mg/天)后运动症状显著改善...运动不能-强直综合征左侧重于右侧,左侧低张性体态,30岁起躯干和四肢出现多发性无痛性脂肪瘤。MRI和肌肉活检正常,脂肪瘤皮肤活检示良性血管脂肪瘤。患者II-5的哥
-

-
2020.03.17 ETV 换用 TAF 治疗使 S 抗原进一步下降 HBV-DNA 转阴一例报告
,肾功,乙肝病毒标志物定量检测.HBVDNA 精准检测。TAF 丙酚替诺福韦治疗三个月后查:S 抗原显著下降,HBVDNA 转阴,6 个月、9 个月、12 个月 S 抗原是逐渐下降至<10IU/ml。S 抗原转阴。表 1 TAF 丙酚替诺福韦治疗中
-

-
2016.02.23 心电图挑战:规律中的不规则心律
间期的 P 波(+)在 I、II、aVF、V4-V6 导联是直立的,PR 间期恒定(0.14s),提示为窦性 P 波,而紧随短 RR 间期的 P 波(^)在 I、II、aVF、V4-V6 导联是倒置的,因此并非窦性 P 波,而是起源于心房其它位置,属于房性早搏,其 PR 间期稍延长但仍恒定(0.20s)。综上,该心电图
-

-
2019.06.25 降钙素原检测试剂盒 B∙R∙A∙H∙M∙S PCT-Q
介绍 :通过半定量免疫色谱法检测降钙素原,可用来诊断及监测严重细菌感染和脓毒症的治疗。包装规格为 25 人份/盒。作为一种半定量检测方法,B·R·A·H·M·S PCT-Q 在各个浓度范围都与 B·R·A·H·M·S PCT LIA 具有紧密相关性。3. 产品特点及优势:√ 德国原研,具有可溯源性√ 无需设备支持,操作
-

-
2012.11.21 抗疟疾药物RTS,S进行中的III期临床研究发布新消息
2012年11月9日,新英格兰医学杂志在网上发布的一个关键、大规模III期临床研究结果显示,疟疾候选疫苗RTS,S能够帮助非洲的婴幼儿防治疟...一直朝着这个目标努力。该研究证明了RTS,S能够帮助婴幼儿防治疟疾。更重要的是,除了使用蚊帐,我们终于找到了一种积极应对疟疾的新方法。”
-

-
2012.11.03 廖旺军:S-1在进展或复发的结直肠癌 化学治疗中的地位
OS (ITT population)-28背景-22S_1奥沙利铂 (SOX) 对比卡培他滨 奥沙利铂 (COX)治疗晚期结直肠癌:III 期研究-07S_1在进展或复发的结直肠癌化学治疗中的地位-01毒性
-

-
2012.08.13 TRC105治疗晚期癌症的耐受剂量为10mg/kg/周
用于晚期难治性实体肿瘤患者的安全性、药动学及其抗肿瘤活性,来加州大学洛杉矶分校医学系的Lee S. Rosen和杜克大学医学中心的Herbert I....。在正在进行中的临床Ib期与临床II期研究中,未在TRC105(来源:中国仓鼠卵巢细胞)治疗的患者中检测到TRC105抗体。在45例可评价患者中,有21例出现病情
-

-
2020.02.20 乳腺癌患者管理创新,辉瑞推出「S.A.F.E. 患者安新服务」
上海,2020 年 2 月 20 日——辉瑞今日宣布携手各方升级乳腺癌患者全程关爱服务,推出创新的「S.A.F.E 患者安新服务」,患者一键扫码便可获得权威...和社会各方力量推出「S.A.F.E 患者安新服务」,把六个患者服务项目的二维码及服务热线信息整合成一个二维码入口,同时通过辉瑞小药箱公众号推出「购药地图」信息
-

-
2014.03.04 糖尿病合并Down’s综合征及毒性弥漫性甲状腺肿1例报告
,Murphy’S征(-),麦氏点压痛可疑(+),移动性浊音(-),未见Grey-Turner征。肠鸣音正常,双肾区无叩击痛。右臀皮肤可见大小约...。染色体核型检查:46,XX,-14,+t(14q21q)(G带核型)。诊断:T1DM合并DKA;21-三体(Down’s)综合征;毒性弥漫性
-
电子科技大学附属医院·四川省人民医院及成都医学会超声专科分会将于2014年3月28日~3月30日在成都市四川省人民医院内举办超声造影暨超声介入诊断及治疗研讨班,该班为省级继续医学教育项目(编号14-22-0902246),授予省级II类医学教育学分4分。届时将邀请北京301医院梁萍教授、广州
-
-
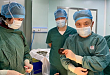
2021.01.27 同济大学附属同济医院成功为一患者植入全皮下心脏除颤器(S-ICD)
主任医师和毛玉副主任医师所在的起搏小组进行了多方评估和分析,对患者进行了体表心电图向量筛查,决定对患者施行全皮下心脏除颤器植入手术。全皮下心脏除颤器(S...。 而全皮下心脏除颤器(S-ICD)由一个脉冲发生器和一根皮下电极组成,无需经静脉路径,也不需要将电极导线放在心腔内,只是将脉冲发生器植入患者腋下的皮肤下面
-
2012.09.19 北京凯诺脊椎矫正培训班
的专业,因此,我们将在WHO教学规划的指导下,采取由浅入深,循序渐进的教程(学时:全程矫正技术I技能班50学时、矫正技术II与X光片分析班50学时、高级矫正学技术班:50学时),使学员易于掌握、逐步提高。一、培训目标(全程矫正技术I技能手法班、矫正技术II与X线分析班、高级矫正学技术班):
